* Call by Value 와 Call by Reference 의 차이점
- Call by Value는 값을 복사하는 것이고, Call by Reference는 주소값을 복사하는 것이다.
- 참고로 자바는 Call by Value 방식을 사용하며, Call by Reference 는 존재하지 않음.
the Java authors choose to only include one simple idea - pass-by-value,
with no default values or optional parameter (overloading often provides a satisfactory alternative),
no variable length parameter lists (added finally in Java 5),
no named parameters, no pass-by-reference, no const (a general Java issue) parameters, etc.
-The Java Programming Language, 2nd ed. by Ken Arnold and James Gosling, section 2.6.1, page 40, 3rd paragraph.
/* 자바는 함수나 메서드의 매개변수 전달 방식에서 단순성을 추구함. 즉 "값에 의한 전달" 만을 지원하며, 다른 복잡한 기능들은 제외됨. */
* Call by Value
- "값만" 전달하는 방식.
- 전달받은 값을 복사하여 처리함. 전달받은 값을 변경하여도 원본은 변경되지 않음.
* Call by Reference
- "참조"에 의한 호출
- 전달받은 값을 직접 참조한다. 전달받은 값을 변경하면 원본도 같이 변경된다.
public class MyClass {
int value;
MyClass(int value) {
this.value = value;
}
public static void swap(MyClass x, MyClass y) {
int temp = x.value;
x.value = y.value;
y.value = temp;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyClass num1 = new MyClass(10);
MyClass num2 = new MyClass(20);
System.out.println("Before Call Method : num1 = " + num1.value + ", num2 = " + num2.value);
swap(num1, num2);
System.out.println("Before Call Method : num1 = " + num1.value + ", num2 = " + num2.value);
}
}- class(reference type) 끼리의 값 변경은 call by reference 로 변경된다.
* Java에 Call by Reference에 없지만 활용되는 이유.
- 기본형(primitive type) : Boolean Type, Numeric Type( short, int, log, float, double, char )
- 참조형(reference type) : Class Type, Interface Type, Array Type, Enum Type 기본형 제외 모든 타입
public class main
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int var = 1;
int[] arr = { 1 };
// call by value
add_value(var);
System.out.println("primitive type : " + var); // 1 : 값 변화가 없음
// call by reference
add_reference(arr);
System.out.println("reference type : " + arr[0]); // 101 : 값이 변화함
}
static void add_value(int var_arg) {
var_arg += 100;
}
static void add_reference(int[] arr_arg) {
arr_arg[0] += 100;
}
}
* 결과
primitive type : 1
reference type : 101
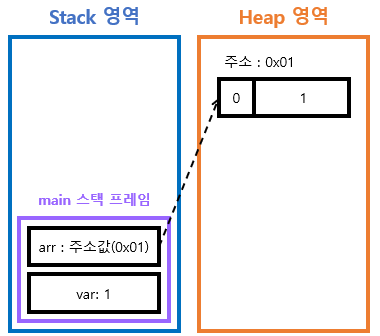
- 기본형은 stack의 변수 안에 value 저장. ( 원시값이 저장됨 )
- 참조형은 stack의 변수 값에는 객체의 주소 값, 객체는 별도의 Heap영역에 저장. ( 실제 데이터는 heap에, stack에 주소값이 저장됨 )

- add_value 내 var_arg가 바뀜.
- var 자체가 바뀐것 아님.
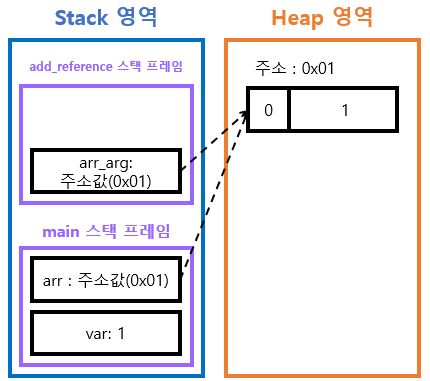
* 정리
- Java는 C와 달리 포인터를 철저하게 숨겨 개발자가 직접 메모리 주소에 접근하지 못하게 했기 때문에 call by reference라는 개념이 존재하지 않는다.
- 위의 예시를 보면 두 변수 안에는 같은 주소를 가지고 있을 뿐 두 변수는 서로 별도로 분리되어 존재함.
add_reference() 호출 시 arr의 주소값을 담아 새로운 변수를 선언함. 이는 단순 히 주소값의 복사이다.
- 각 변수는 서로 다른 scope에 존재한다.
'Computer Science > OS' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Process 와 Thread 개념 (0) | 2024.11.22 |
|---|
